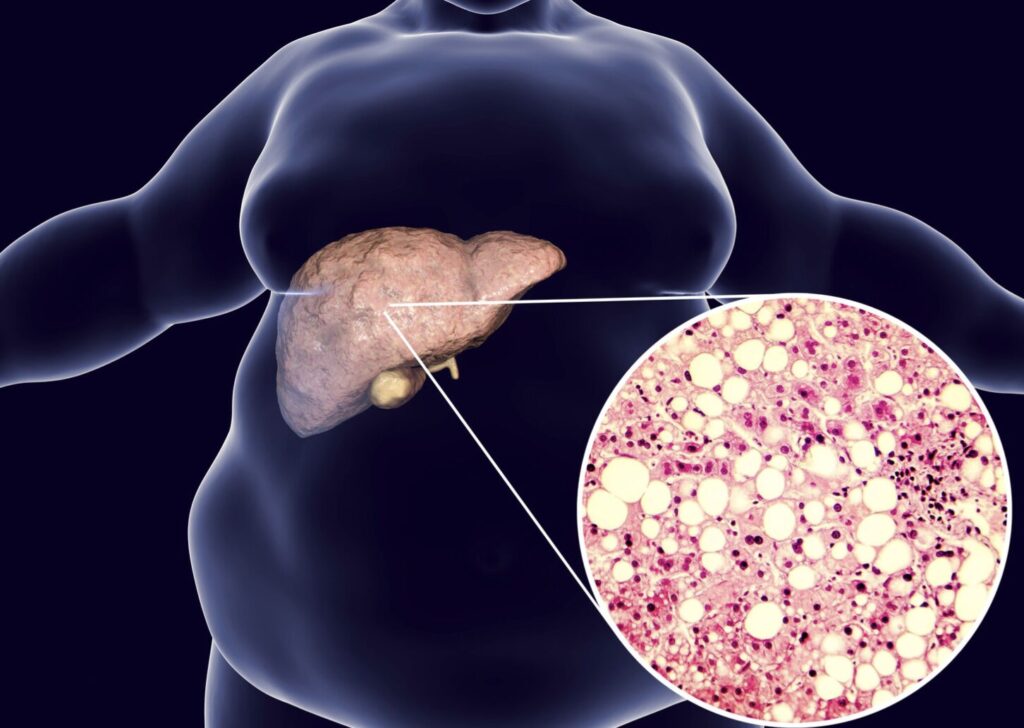
Excess fat accumulates in the liver cells, causing fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis. Although some fat is normally present in the liver, too much of it can interfere with normal liver function and eventually cause inflammation, scarring, or even more serious liver damage.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are the two primary forms of fatty liver disease. While AFLD is mostly linked to heavy alcohol use, NAFLD is the more prevalent kind and is linked to metabolic risk factors such obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
In order to manage the illness and support liver health, it can be really important to comprehend the reasons of fatty liver and the natural therapy alternatives that are available.
Fatty Liver Disease Causes
- Obesity: One of the main causes of fatty liver is excess body weight. Inflammatory substances released by fat cells have the potential to damage liver tissue and worsen the buildup of fat in the liver.
- Poor Diet: Fatty liver can develop as a result of a diet heavy in processed foods, sugar, refined carbohydrates, and harmful fats. Fat deposition results from the burden that eating too many calories and harmful fats puts on the liver.
- Insulin Resistance: Frequently linked to type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance can hinder the liver’s capacity to metabolise fat and cause the liver to store fat.
- Excessive Alcohol Use: Alcoholic fatty liver disease can occur as a result of long-term alcohol use that damages liver cells and interferes with fat metabolism.
- High Triglycerides and Cholesterol: People who have high blood levels of triglycerides and cholesterol are more likely to develop fatty liver disease because they can cause the liver to accumulate more fat.
- Genetics: Fatty liver disease can also occur as a result of genetic predisposition and family history. It’s possible that certain people are genetically predisposed to liver fat accumulation.
- Drugs: A number of medications, including corticosteroids, some antidepressants, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause the development of fatty liver.
- Other Conditions: Because they affect hormones and metabolism, conditions like sleep apnoea, hypothyroidism, and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) can raise the risk of fatty liver disease.

Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
Fatty liver disease may not show any symptoms at all in its early stages. But when the illness worsens, people could encounter:
The upper right side of the abdomen may feel full or uncomfortable. Weakness or exhaustion
Inexplicable loss of weight
- Jaundice (eye and skin yellowing)
Dark urine; leg or abdominal swelling
Fatty liver can develop into more serious diseases like cirrhosis or liver cancer if treatment is not received.
Natural Methods of Treating Fatty Liver
Certain lifestyle modifications and natural therapies can greatly aid in the management of fatty liver disease and even reverse its course, even if medical treatment is frequently required. The following are a few of the best natural therapy methods:
- Adopt a balanced, healthful diet: – Increase your consumption of fibre by including foods high in fibre, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. Fibre promotes better digestive function and lessens liver fat accumulation.
Limit processed meals and refined sugars: Cutting back on sugar, particularly fructose, can help keep the liver from gaining fat. Minimise processed foods, such as drinks and sugary snacks.
Eat fats that are good for you: Healthy fats like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil can be used to replace saturated fats. Fatty fish, such as salmon, provide omega-3 fatty acids, which can help lower liver fat.
- Boost antioxidants: Antioxidant-rich foods, like leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli and Brussels sprouts), and berries, can help lower oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Physical activity is essential for lowering hepatic fat accumulation. Walking, cycling, and swimming are examples of aerobic exercises that increase insulin sensitivity and burn fat.
Weightlifting and other strength training activities can increase muscle mass and help control blood sugar, both of which are good for the liver. - Reduce Excess Weight Gradually: Liver fat can be considerably decreased by losing 5–10% of body weight. However, rapid weight loss should be avoided because it can cause further liver stress. The safest method is to lose weight gradually and steadily.
- Herbal Treatments: – Milk Thistle: This herb includes silymarin, a substance with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities. According to research, milk thistle may support liver regeneration and protection.
Turmeric: Turmeric’s key ingredient, curcumin, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It might encourage fat metabolism and lessen liver inflammation.
Dandelion Root: It is thought to promote liver detoxification and enhance bile production, both of which can facilitate fat metabolism.
Ginger: Studies have demonstrated that ginger helps to maintain liver health and lower inflammation. Drinking ginger tea or including fresh ginger in your diet may help lower liver fat. - Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration facilitates digestion and helps remove toxins from the liver. The liver will operate at its best if you drink lots of water throughout the day.
- Avoid Alcohol: It is imperative that people with alcoholic fatty liver disease completely stop drinking alcohol. Limiting alcohol use can enhance liver function and stop more liver damage.
- Handle Stress: Prolonged stress can make liver issues worse by causing hormonal imbalances and inflammation. Deep breathing, yoga, meditation, and other relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and enhance general health.
- Make Sure You Get Enough Sleep: Increased liver fat has been connected to inadequate sleep. For liver regeneration and general health, try to get 7–9 hours of good sleep per night.
- Prevent Toxins: Reduce your exposure to environmental toxins that might further tax your liver, such as pesticides, home chemicals, and air pollution.
In conclusion
If left untreated, fatty liver disease, a common disorder, can have major repercussions. However, the liver can frequently recover and regenerate if proactive measures are taken.
People can promote liver health and lessen the effects of fatty liver disease by eating a balanced diet, exercising, decreasing weight gradually, and implementing specific herbal and lifestyle modifications. Before beginning any new treatment, always get advice from your healthcare professional, particularly if you already have a medical problem.
Long-term liver health can be promoted and fatty liver disease can be prevented or even reversed with a mix of natural therapies and lifestyle changes.