The management of hypothyroidism can be complex, as it necessitates the careful coordination of hormone therapies alongside dietary considerations. Although there is no specific “hypothyroidism diet,” certain foods may adversely affect thyroid function and the efficacy of medication. The following nine foods are recommended for avoidance or limitation in individuals with hypothyroidism, as advised by medical professionals and nutritionists.
- Soy-Based Products
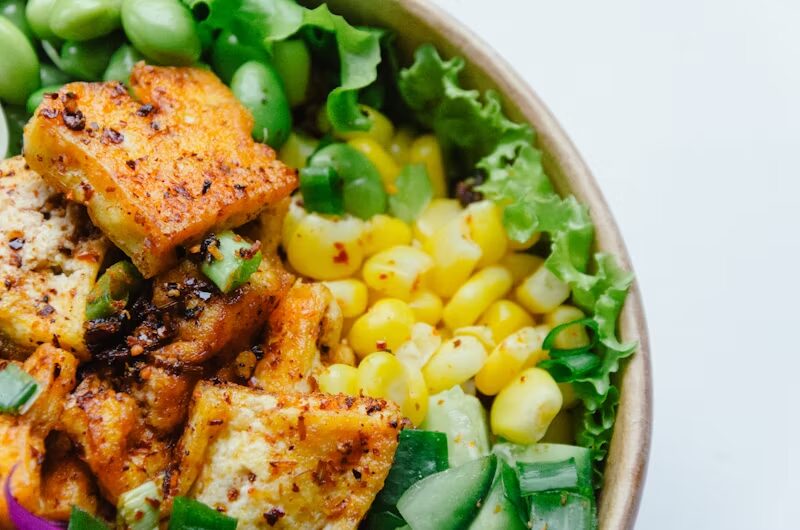

Soy contains isoflavones, which are compounds that may disrupt the assimilation of iodine, an essential nutrient for optimal thyroid function. Research has indicated that soy products, including tofu, edamame, and soy milk, may influence the absorption of thyroid hormones, particularly when ingested in proximity to the timing of medication administration. To mitigate potential risks, it is advisable to wait a minimum of four hours after the consumption of soy-based foods prior to administering your thyroid medication.
It is advisable to consider the inclusion of plant-based proteins, such as lentils or legumes, which are less likely to adversely affect thyroid function.
- Cruciferous Vegetables
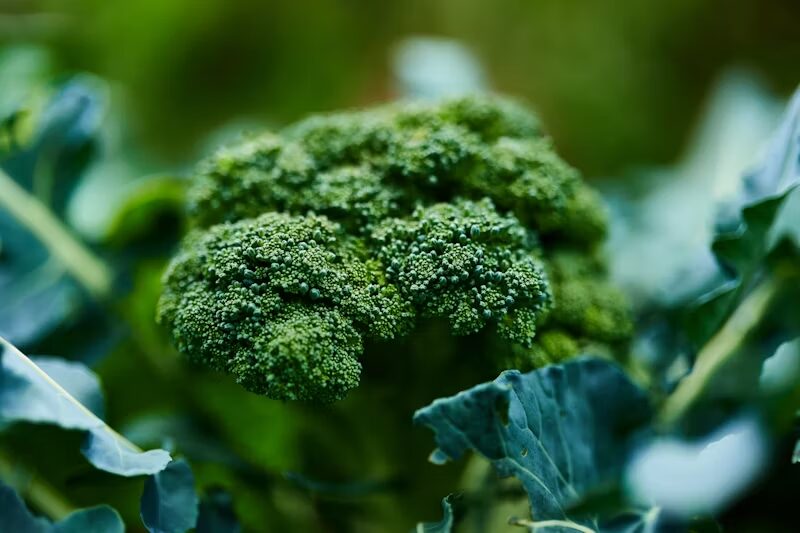

Raw cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, contain goitrogens, which are compounds that may impede the utilisation of iodine. Although these vegetables are abundant in nutrients, the consumption of them in substantial amounts in their unprocessed state may inhibit thyroid function.
Conversely, the preparation of cruciferous vegetables through cooking can effectively inactivate the majority of goitrogens, thereby rendering them safer for moderate consumption.
- Gluten

Numerous individuals diagnosed with hypothyroidism, especially those suffering from Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, frequently exhibit coexisting conditions such as coeliac disease or gluten sensitivity. Gluten has the potential to induce inflammation, which may exacerbate thyroid disorders and impede the absorption of medications.
It is advisable to undergo testing for gluten sensitivity or coeliac disease. If necessary, consider substituting with gluten-free grains such as quinoa or rice.
- Processed Food Products

Processed foods frequently possess elevated sodium content, which can intensify the risks associated with hypothyroidism, such as hypertension. Furthermore, these foods are deficient in essential nutrients and may exacerbate inflammation. It is advisable to refrain from consuming frozen meals, pre-packaged munchies, and fast food options.
Alternatively, one may opt for whole, minimally processed foods such as organic fruits and vegetables.
- Confectionery Delights

Hypothyroidism diminishes metabolic activity, thereby facilitating weight gain. Sugary foods such as confections, baked goods, and carbonated beverages offer inert calories that may lead to weight gain and exacerbate fluctuations in energy levels.
It may be advisable to consider utilising natural sweeteners such as honey or indulging in fruits, particularly berries, to fulfil your craving for sweetness.
- Foods Rich in Fat

Fried foods, fatty cuts of meat, and spreads such as butter or margarine may hinder the body’s capacity to assimilate thyroid hormone replacement medications effectively. Diets high in fat may also diminish the efficacy of hormone production by the thyroid gland.
Alternatively, consider incorporating lean proteins into your diet and utilising heart-healthy oils, such as olive or avocado oil, for cooking purposes.
- Coffee

Caffeine has the potential to inhibit the absorption of thyroid medication if ingested shortly after administration. Research indicates that individuals who consume coffee in conjunction with their medication frequently experience erratic thyroid hormone levels.
It is advisable to ingest your medication with water and to allow a minimum interval of 30 minutes before consuming coffee.
- Ethanol

Alcohol consumption can interfere with the levels of thyroid hormones as well as the thyroid gland’s capacity to synthesise these hormones. Prolonged alcohol consumption may exacerbate the symptoms of hypothyroidism or impede the efficacy of treatment.
Alternatively, consider moderating your alcohol consumption or abstaining entirely to alleviate stress on your thyroid gland.
- Specific Fruits and Nuts

Goitrogenic fruits, such as peaches, pears, and strawberries, have the potential to impede the absorption of iodine. In a similar vein, legumes such as almonds and walnuts may exhibit a slight goitrogenic effect.
It is advisable to concentrate on the consumption of fruits abundant in antioxidants, such as blueberries and cherries, while also moderating the intake of almonds to harmonise their advantages with any potential effects on thyroid function.
Strategies for the Management of Hypothyroidism

Although these foods may aggravate symptoms, a diet conducive to thyroid health need not be restrictive. Complement your meal plan with foods that are abundant in selenium, such as Brazil nuts, and zinc, which can be found in lean meats and legumes, to promote optimal thyroid health. It is imperative to consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian in order to develop a balanced dietary plan that is tailored to your individual requirements.
Dietary modifications can significantly contribute to the management of hypothyroidism. By comprehending which foods to restrict or eliminate, you can more effectively promote your thyroid health and enhance your overall well-being. It is imperative to seek the counsel of a healthcare professional prior to implementing any substantial modifications to your diet.